Technical Glossary
Diesel Power Generator
A diesel generator is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine generator. A diesel compression-ignition engine is usually designed to run on diesel fuel.

Glossary
General Terms
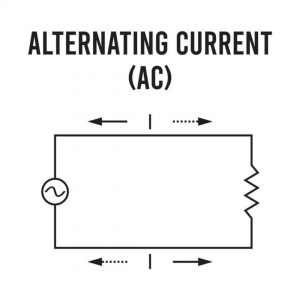
Alternating Current (AC) : Current flowing from zero to a positive maximum and then back to zero, flows down again to a negative maximum to return back to zero.
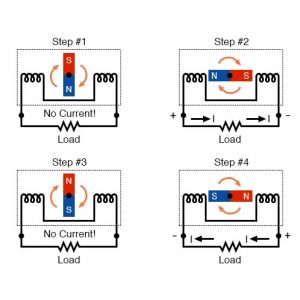
AC Alternators : If a machine is constructed to rotate a magnetic field around a set of stationary wire coils with the turning of a shaft, AC voltage will be produced across the wire coils as that shaft is rotated, in accordance with Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction. This is the basic operating principle of an AC generator, also known as an alternator.
Diesel Engine : An internal combustion engine in which fuel oil is burnt by heat produced from air compression. The most commonly bought Industrial Diesel Engines are either Rebuilt Diesel Engine or Used Diesel Engine.
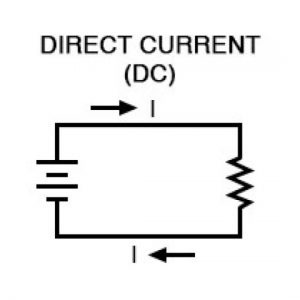
Direct Current (DC) : Current produced by storage battery or electromagnetic induction, with a unidirectional flow.
Standby Generators : is a backup power solution that provides power to your business operations, commercial & industrial applications, or facilities in the event of a power outage. Standby generators are a robust solution that can provide power for days during extended power outages, depending on the fuel type and configuration of the generator.
Synchronization Panels are mainly designed and used to meet power system requirements. These panels function both manually and with an automatic synchronizing function for two or more generators or breakers. They are widely used in synchronizing generators and offering multiplex solutions.
Glossary
Generators Parts
Adapters: This is a device that will connect pieces of equipment that cannot be directly connected
Air Cleaner Assembly: Protective covering that protects the air filter from harsh elements that could weaken and damage it.
Alternator: This device converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Anti Vibration Mounts: Flexible supports for an engine that reduces the amount of noise and vibration.
Axles: A rod or spindle passing through the center of a wheel
Base Tank: A large gas tank that is placed under the generator itself
Battery Charge Rectifier: This component changes AC voltage from the battery charge windings to DC voltage for charging a battery.
Brush: This graphite or copper made conducting element maintains sliding electrical contact between static and moving element.
Circuit Breaker: Automatic device for stopping the flow of electricity as a safety measure.
Core: The magnetic structure built lamination in the generator.
Cradle: Covering a generator or engine, this metal frame provides extra protection from outer disturbances.
Flywheel: Storing energy in a rotating mass form, Flywheel is a very active substitution of chemical batteries.
Hour Meter: Meter that measures and tracks the amount of hours a generator runs.
Ignition Coil: Supplies DC voltage to the spark plugs.
Magneto: Built with permanent magnets, Magneto is a special kind of alternator that generates current for ignition in an internal combustion engine
Rectifier: Rectifier is used for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
Relay: Normally used in control circuits, relay is a switch driven by electricity and rules over contactor by virtue of low amperage contacts.
Rotor: Rotor is the element that on, which the rotating of a generator depends.
Rotor winding: Comprises of all the rotor pole windings and connections.
Stator: Stator is the static or unmovable element of a generator.
Stator winding: Comprises of stator coils with their interconnections.
Switchgear: Equipment that can be used in the transmission of electricity.
Transformers: An apparatus for reducing or increasing the voltage of an alternating current.
Voltage Regulator: By modulating the flow of DC to the rotor, Voltage regulator maintains optimum generator voltage, automatically.
Winding: Winding comprises all the coils of a generator.


Glossary
Generators Systems
Air Filter: Filters out moisture, dust, rust, etc. From the compressed air.
Arc: The flow of electricity across an open gap.
Grid: In order to meet the power needs at the grids in different points, a system of power lines and generators, interconnected is used. This is a grid.
Load: Load is that the amount of electric power used by devices associated to electricity generating system.
Off-Peak: A specific period when power demand of a system is comparatively low. Counted from 10 p.m. until 6 a.m., from Monday through Saturday and during the whole day on Sunday by NERC.
Off-Peak Rate: This is the rate of cost for power used during Off-Peak periods.
Pad: Concrete pads are installed in the ground outside of a building, often including vibration insulators, to place the generator on top of.
Peak: Measurement of the maximum load that is consumed within a specified time period.
Phase: Phase measures the uniform periodic change in amplitude or magnitude of an alternating current.
Rated Voltage: The specific voltage measurement at which an engine generator set can start functioning.
Single Point of Failure: Single point of failure is a location in a redundant system where a single powers failure results in loss of electrical power to the critical load.
Standby (Backup) Service: Service through a permanent connection not normally used but available in lieu of, or as a supplement to, the usual source of supply.
Standby Power: This is the backup source of electrical energy that remains dormant and starts functioning as soon as a control device instructs it to.
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply): Supplies power automatically and instantly during shortage of power supply. UPS operation is dependent on a primary power source such as the electric utility grid, as it does generate power itself.
Glossary
Electric Power Units
Amperage: Measurement of the strength or intensity of an electric current in ampere.
Frequency: The number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Cycles per second
Hertz (Hz): Unit of frequency that is equal to one cycle per second.
Inertia: The property of an object to remain at rest or remain moving unless acted upon by some outside source. In motors, inertia refers to the driven load. Once a load is in motion in amount of power to keep it in motion is reduced.
Joule: Measurement of electrical energy equivalent to the work done when a current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second.
Kilowatt (KW): Kilowatt is power needed to do work at the rate of 1000 joules per second.
Kilowatt-hour (KWhr): Total number of kilowatts used per hour. Or 3,600,000 joules.
KVA: KVA is kilovolt-ampere and is the unit of apparent power. KVA is used for measuring the power consumption of non-resistive equipment such as motors, computers, and most non-incandescent lighting.
Pole: The number of sets of three-way electromagnetic windings that a motor has.
OHM: Unit of electrical resistance. Once volt will cause a current of one flow through a resistance of one ohm.
RPM: Revolutions Per Minute
Volt: Potential difference between two points.
Voltage: Measurement of electrical potential difference expressed in volts.
Watt: Measurement of electrical power. One watt is equal to 1 joule of energy per second.


Glossary
Organization & Abbreviations
APPA: American Public Power Association A national service organization that represents 2000 municipal and other state or local publicly owned electric utilities spread across the United States.
CAA: Clean Air Act
CFR: Code of Federal Regulations The codification of the general and permanent rules and regulations published by the Federal Register by the executive departments.
DOC: Diesel oxidation catalyst Designed to oxidize carbon monoxide, gas phase hydrocarbons, and the SOF fraction of diesel particulate matter to CO2 and H20.
DR: Demand Response Voluntary PJM program that compensates end-use costumers for reducing their electricity use when the reliability of the grid is threatened.
EPA: Environmental Protection Agency An agency of the US government which was created for the purpose of protecting human health and the environment.
ESP: Emergency Standby Power An independent source of electrical power that supports important electrical systems on loss of the normal power supply.
NSPS: New source performance standards Technology-based standards implemented by the EPA.
NESCAUM: National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants Emission standards set by the US EPA.
PM: Particulate Matter The sum of all solid and liquid particles suspended in air.
RCRA: Resource and Conservation and Recovery Act The principal federal law in the US governing the disposal of solid waste and hazardous waste.
RICE: Reciprocal Internal Combustion Engines Any internal combustion engine which uses reciprocating motion to convert heat energy into mechanical work.
SI: Spark Ignition Internal combustion engine where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a park from a spark plug.